1. 概述
mAP 是评价目标检测模型模型好坏的重要指标,这篇文章就介绍下如何计算 mAP 。
2. 基本概念
介绍 mAP 计算之前首先我们先了解几个重要概念。
2.1. IOU
IOU 是 Intersection over Union 的缩写,意为交并比。它用来衡量真实边界框与预测边界框的重合程度,它的计算公式为 [交集/并集] 。
2.2. 精确率和召回率
介绍精确率和召回率的之前先了解 TP 、 TN 、 FP 、 FN 这几个概念。
TP: True Positive 的缩写,意思是预测为正样本,实际上也为正样本。
TN: True Negtive 的缩写,意思是预测为负样本,实际上也是负样本。
FP: False Positive 的缩写,意思是预测为正样本,实际上是负样本。
FN: False Negtive 的缩写,意思是预测为负样本,实际上是正样本。
以上这四个值很好理解,就是非常容易搞混,可以这样记: T 和 F 代表的是该样本是否被正确分类; P 和 N 代表的是该样本被预测成了正样本还是负样本。
有了以上概念之后,精确率和召回率就很好理解了。
精确率 = TP / TP + FP : 表示分类器认为是正类并且确实是正类的部分占所有分类器认为是正类的比例。
召回率 = TP / TP + FN : 表示分类器认为是正类并且确实是正类的部分占所有确实是正类的比例。
2.3. 置信度
置信度为 pr(object)*iou(b,object) ,表示预测边界框是否包含物体与物体与真实边界框的 IOU 的乘积。置信度用来表示模型输出的可信度,如果置信度设置的高的话,预测的结果和实际情况就很符合,如果置信度低的话,就会有很多误检测。
3. AP 的引入
为什么要引入 AP 这个概念呢?让我们看下对于一个模型的好坏如果只使用精确率或者召回率会有什么问题。假设一幅图像里面总共有 3 个正样本,目标检测对这幅图的预测结果有 10 个,其中 3 个实际上是正样本, 7 个实际上是负样本。对应置信度如图所示:
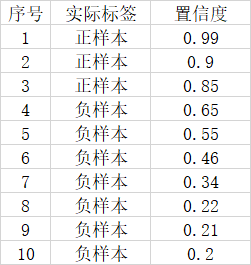
如果我们将可以接受的置信度设置为 0.95 的话,那么目标检测算法就会将序号为 1 的样本作为正样本,其它的都是负样本。此时 TP = 1 , FP = 0 , FN = 2 。那么精确率 = 1 ,召回率 = 1/3 。
此时精确率非常高,但是事实上我们只检测出一个正样本,还有两个没有检测出来,因此只用精确率就不能很好的表示模型的好坏。
如果我们将可以接受的置信度设置为 0.35 时,目标检测算法就会将序号为 1 到 6 的样本都作为正样本,其它的是负样本。此时 TP = 3 , FP = 3 , FN = 0 。那么精确率 = 1/2 ,召回率 = 1 。
此时召回率非常高,但是事实上目标检测算法认为是正样本的样本里面,有 3 个样本确实是正样本,但有 3 个是负样本,存在非常严重的误检测,因此只用召回率也不恶嗯呐很好的表示模式的好坏。
基于以上单个指标的局限性,引入了 AP , AP 指的是利用不同的精确率和召回率的点的组合,画出来的曲线下面的面积。 当我们取不同的置信度,可以获得不同的精确率和召回率,当我们取得置信度够密集的时候,就可以获得非常多的精确率和召回率。此时精确率和召回率可以在图片上画出一条线,这条线下部分的面积就是某个类的 AP 值。 mAP 就是所有的类的 AP 值求平均。
4. AP 的代码实现
这里介绍的参考代码来自 Github 。在使用这个代码进行 mAP 计算之前需要做些准备工作。
首先,准备预测结果,并放到 detection-results 中。
然后,准备标签文件,并放到 ground-truth 中。
最后,准备图片文件,并放到 image-optional 中。这个目录用来做可视化,可以没有。
这里我先假设以上文件已准备好,并且这里假设不做可视化,下面我们直接看代码实现:
首先初始化已经准备好了的目录。
os.chdir(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
GT_PATH = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'input', 'ground-truth')
DR_PATH = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'input', 'detection-results')
IMG_PATH = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'input', 'images-optional')
- 创建两个目录, .temp_files 是临时目录,存放计算过程中的临时数据; output 存放最终的计算结果。
TEMP_FILES_PATH = ".temp_files" if not os.path.exists(TEMP_FILES_PATH): os.makedirs(TEMP_FILES_PATH) output_files_path = "output" if os.path.exists(output_files_path): shutil.rmtree(output_files_path) os.makedirs(output_files_path)
接下来是遍历所有标签文件,将每个标签文件里的目标解析出来,放到 _ground_truth.json 中。
- 获得所有标签文件的列表,然后排序。
- gt_counter_per_class: 记录每个类别标签的个数。
- counter_images_per_class: 记录每一类别存在于多少张图像中。
ground_truth_files_list = glob.glob(GT_PATH + '/*.txt') ground_truth_files_list.sort() gt_counter_per_class = {} counter_images_per_class = {} - file_id: 去掉后缀的文件名
- temp_path: file_id 对应的预测值文件
- lines_list: 读取标签文件的每一行
- bounding_boxes: 存储标签信息
- is_difficult: 目标是否是难检测样本
- already_seen_classes: 某一类别的样本是否在一张图像中多次出现
- 解析标签文件的每一行,格式为 class_name, left, top, right, bottom, _difficult , _difficult 可能没有
- 将解析出来的信息添加到 bounding_boxes 中
- 难检测样本不记录到个数里
- gt_counter_per_class: 记录每一个类总共有多少个样本
- already_seen_classes: 某一类别的样本是否在一张图像中多次出现,如果某一类别在一张图像中没有出现过,则 counter_images_per_class 加 1 , counter_images_per_class: 记录每一类别存在于多少张图像中
- 将解析出来的信息写入 file_id + _ground_truth.json 文件中
gt_files = [] for txt_file in ground_truth_files_list: file_id = txt_file.split(".txt", 1)[0] file_id = os.path.basename(os.path.normpath(file_id)) # check if there is a correspondent detection-results file temp_path = os.path.join(DR_PATH, (file_id + ".txt")) lines_list = file_lines_to_list(txt_file) bounding_boxes = [] is_difficult = False already_seen_classes = [] for line in lines_list: if "difficult" in line: class_name, left, top, right, bottom, _difficult = line.split() is_difficult = True else: class_name, left, top, right, bottom = line.split() bbox = left + " " + top + " " + right + " " +bottom if is_difficult: bounding_boxes.append({"class_name":class_name, "bbox":bbox, "used":False, "difficult":True}) is_difficult = False else: bounding_boxes.append({"class_name":class_name, "bbox":bbox, "used":False}) if class_name in gt_counter_per_class: gt_counter_per_class[class_name] += 1 else: gt_counter_per_class[class_name] = 1 if class_name not in already_seen_classes: if class_name in counter_images_per_class: counter_images_per_class[class_name] += 1 else: counter_images_per_class[class_name] = 1 already_seen_classes.append(class_name) new_temp_file = TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + file_id + "_ground_truth.json" gt_files.append(new_temp_file) with open(new_temp_file, 'w') as outfile: json.dump(bounding_boxes, outfile) - 记录所有的类别并排序,保存类别个数
gt_classes = list(gt_counter_per_class.keys()) gt_classes = sorted(gt_classes) n_classes = len(gt_classes)
遍历所有预测信息文件,将预测为同一类别的信息保存到一个文件中。
- 获得预测信息文件,并排序
dr_files_list = glob.glob(DR_PATH + '/*.txt') dr_files_list.sort() - 遍历每一个类别,统计所有预测类别为该类别的信息,将信息保存到 bounding_boxes 中
- 将 bounding_boxes 按照置信度排序
- 将每个类别的所有信息保存到 class_name + _dr.json 文件中
for class_index, class_name in enumerate(gt_classes): bounding_boxes = [] for txt_file in dr_files_list: file_id = txt_file.split(".txt",1)[0] file_id = os.path.basename(os.path.normpath(file_id)) temp_path = os.path.join(GT_PATH, (file_id + ".txt")) lines = file_lines_to_list(txt_file) for line in lines: tmp_class_name, confidence, left, top, right, bottom = line.split() if tmp_class_name == class_name: bbox = left + " " + top + " " + right + " " +bottom bounding_boxes.append({"confidence":confidence, "file_id":file_id, "bbox":bbox}) bounding_boxes.sort(key=lambda x:float(x['confidence']), reverse=True) with open(TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + class_name + "_dr.json", 'w') as outfile: json.dump(bounding_boxes, outfile)
准备工作做完了,开始计算 mAP 。
- 将 AP 值写入 output.txt 文件
- count_true_positives: 遍历每个类别,统计每个类别的 tp 个数。
- 取出之前保存的每个类别的预测信息
- 遍历每一条预测信息
- 根据 file_id 找到对应的标签信息
- 获取预测的边界框信息和标签的边界框信息,计算 IOU 值,找到最佳的 iou 值
- 如果 iou 大于等于给定的最小 iou 阈值,且标签信息不是难预测的样本,表示该预测为正类且预测正确
- gt_match[“used”]=False: 表示该标签被用过后就不能在重复使用,如果已被使用,则为假正类 fp[idx] = 1
- 如果 iou 小于给定的最小 iou 阈值,则为假正类 fp[idx] = 1
- 计算精确率和召回率,统计假正类的个数,统计真正类的个数
- 召回率=真正类个数/所有正样本的个数
- 精确率=真正类个数/所有预测为正类的个数
- AP 为召回率和精确率围成的曲线的面积,使用 voc_ap 函数计算各个类的 AP
- mAP = sum_AP / n_classes: mAP 是所有类别 AP 的平均值。
sum_AP = 0.0 ap_dictionary = {} lamr_dictionary = {} with open(output_files_path + "/output.txt", 'w') as output_file: output_file.write("# AP and precision/recall per class\n") count_true_positives = {} # 遍历每个类别 for class_index, class_name in enumerate(gt_classes): count_true_positives[class_name] = 0 dr_file = TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + class_name + "_dr.json" dr_data = json.load(open(dr_file)) nd = len(dr_data) tp = [0] * nd # creates an array of zeros of size nd fp = [0] * nd for idx, detection in enumerate(dr_data): file_id = detection["file_id"] gt_file = TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + file_id + "_ground_truth.json" ground_truth_data = json.load(open(gt_file)) ovmax = -1 gt_match = -1 bb = [ float(x) for x in detection["bbox"].split() ] for obj in ground_truth_data: if obj["class_name"] == class_name: bbgt = [ float(x) for x in obj["bbox"].split() ] bi = [max(bb[0],bbgt[0]), max(bb[1],bbgt[1]), min(bb[2],bbgt[2]), min(bb[3],bbgt[3])] iw = bi[2] - bi[0] + 1 ih = bi[3] - bi[1] + 1 if iw > 0 and ih > 0: # compute overlap (IoU) = area of intersection / area of union ua = (bb[2] - bb[0] + 1) * (bb[3] - bb[1] + 1) + (bbgt[2] - bbgt[0] + 1) * (bbgt[3] - bbgt[1] + 1) - iw * ih ov = iw * ih / ua if ov > ovmax: ovmax = ov gt_match = obj # set minimum overlap min_overlap = MINOVERLAP if ovmax >= min_overlap: if "difficult" not in gt_match: if not bool(gt_match["used"]): # true positive tp[idx] = 1 gt_match["used"] = True count_true_positives[class_name] += 1 # update the ".json" file with open(gt_file, 'w') as f: f.write(json.dumps(ground_truth_data)) else: # false positive (multiple detection) fp[idx] = 1 else: # false positive fp[idx] = 1 if ovmax > 0: status = "INSUFFICIENT OVERLAP" # compute precision/recall cumsum = 0 for idx, val in enumerate(fp): fp[idx] += cumsum cumsum += val cumsum = 0 for idx, val in enumerate(tp): tp[idx] += cumsum cumsum += val #print(tp) rec = tp[:] # for idx, val in enumerate(tp): rec[idx] = float(tp[idx]) / gt_counter_per_class[class_name] #print(rec) prec = tp[:] # for idx, val in enumerate(tp): prec[idx] = float(tp[idx]) / (fp[idx] + tp[idx]) #print(prec) ap, mrec, mprec = voc_ap(rec[:], prec[:]) sum_AP += ap text = "{0:.2f}%".format(ap*100) + " = " + class_name + " AP " #class_name + " AP = {0:.2f}%".format(ap*100) """ Write to output.txt """ rounded_prec = [ '%.2f' % elem for elem in prec ] rounded_rec = [ '%.2f' % elem for elem in rec ] output_file.write(text + "\n Precision: " + str(rounded_prec) + "\n Recall :" + str(rounded_rec) + "\n\n") if not args.quiet: print(text) ap_dictionary[class_name] = ap n_images = counter_images_per_class[class_name] lamr, mr, fppi = log_average_miss_rate(np.array(prec), np.array(rec), n_images) lamr_dictionary[class_name] = lamr output_file.write("\n# mAP of all classes\n") mAP = sum_AP / n_classes text = "mAP = {0:.2f}%".format(mAP*100) output_file.write(text + "\n") print(text)