1. 概述
VGG 由 Visual Geometry Group 实验室开发。它提出了可以通过重复使用简单的基础块来构建深度模型的思路。
2. VGG 块
VGG 块的由连续使用数个相同的填充为 1 、窗口形状为 3×3 的卷积层后接上一个步幅为 2 、窗口形状为 2×2 的最大池化层。卷积层保持输入的高和宽不变,而池化层则对其减半。
3. VGG 网络
与 AlexNet 和 LeNet 一样, VGG 网络由卷积层模块后接全连接层模块构成。卷积层模块串联数个 VGG 块,其超参数由变量 conv_arch 定义。该变量指定了每个 VGG 块里卷积层个数和输出通道数。全连接模块则跟 AlexNet 中的一样。
通过堆叠多个 3x3 的卷积核来替代大尺度卷积核(减少所需参数)。可以通过堆叠两个 3x3 的卷积核替代5x5的卷积核,堆叠三个 3x3 的卷积核替代 7x7 的卷积核。也就是拥有相同的感受野。
感受野的计算公式: F(i) = (F(i + 1) - 1) * Stride + Ksize ; F(i) 为第 i 层感受野, Stride 为第 i 层步距, Ksize 为卷积核或池化核尺寸。
3.1 VGG 网络结构
VGG 网络结构如下图所示:
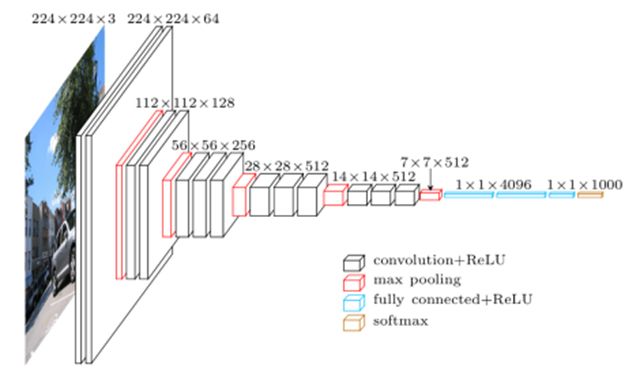
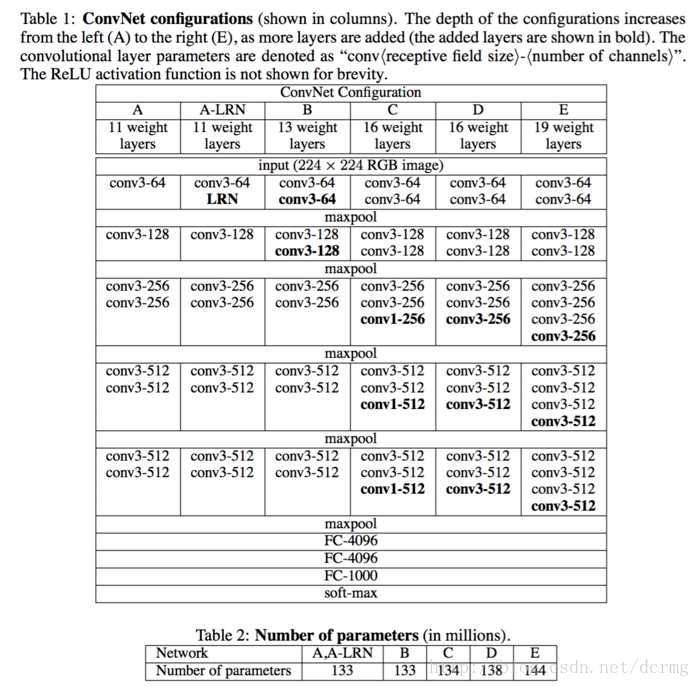
VGG 网络组成如下图所示:
VGG 网络代码实现:
def make_features(cfg: list):
layers = []
in_channels = 3
for v in cfg:
if v == "M":
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(True)]
in_channels = v
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
cfgs = {
'vgg11': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg13': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg16': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg19': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
}
def vgg(model_name="vgg16", weights_path=None):
try:
cfg = cfgs[model_name]
except:
print("Warning: model number {} not in cfgs dict!".format(model_name))
exit(-1)
model = VGG(make_features(cfg), weights_path=weights_path)
return model
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, class_num=1000, init_weights=False, weights_path=None):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(512*7*7, 2048),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(2048, 2048),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(2048, class_num)
)
if init_weights and weights_path is None:
self._initialize_weights()
if weights_path is not None:
self.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path), strict=False)
def forward(self, x):
# N x 3 x 224 x 224
x = self.features(x)
# N x 512 x 7 x 7
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
# N x 512*7*7
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
# nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
# nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)